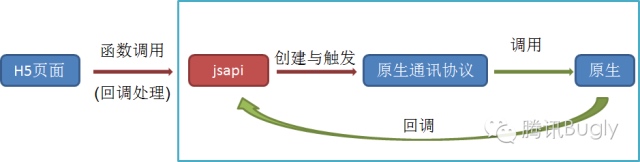
iOS中的HTML交互简说
跟原生开发相比,H5的开发相对来一个成熟的框架和团队来讲在开发速度和开发效率上有着比原生很大的优势,至少不用等待审核。那么问题来了,H5与本地原生代码势必要有交互的,比如本地上传一些信息,H5打开本地的页面,打开本地进行微信等第三方分享等,今天就简单讲一下iOS中本地UIWebView,WKWebView与H5的交互。
DEMO地址:点击下载
##UIWebView的交互
###stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString的使用
UIWebView在2.0时代就有的类,一直到现在(目前9.x)都可以使用的WEB容器,它的方法很简单,在iOS7.0之前JS交互的方法只有一个stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:
- (nullable NSString *)stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:(NSString *)script;
使用stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString方法,需要等UIWebView中的页面加载完成之后去调用.
以下是简单的使用场景:
1、获取当前页面的url。
- (void)webViewDidFinishLoad:(UIWebView *)webView {
NSString *currentURL = [webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"document.location.href"];
}
2、获取页面title:
- (void)webViewDidFinishLoad:(UIWebView *)webView {
NSString *currentURL = [webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"document.location.href"];
NSString *title = [webview stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"document.title"];
}
3、修改界面元素的值。
NSString *js_result = [webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"document.getElementsByName('q')[0].value='iOS';"];
4、表单提交:
NSString *js_result2 = [webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"document.forms[0].submit(); "];
这样就实现了在google搜索关键字:“iOS”的功能。
5、插入js代码
上面的功能我们可以封装到一个js函数中,将这个函数插入到页面上执行,代码如下:
"script.type = 'text/javascript';"
"script.text = \"function myFunction() { "
"var field = document.getElementsByName('q')[0];"
"field.value='iOS';"
"document.forms[0].submit();"
"}\";"
"document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(script);"];
[webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"myFunction();"];
看上面的代码:
a、首先通过js创建一个script的标签,type为'text/javascript'。
b、然后在这个标签中插入一段字符串,这段字符串就是一个函数:myFunction,这个函数实现google自动搜索关键字的功能。
c、然后使用stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString执行myFunction函数。
6、直接调用JS函数
上面的函数调用是本地注入到H5中,然后本地调用的,那么如果H5中就有原生的JS函数:myFunction();,那么我们就可以直接执行:
[webView stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString:@"myFunction();"];
###JavaScriptCore框架的使用
我们会发现stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString的方法调用太笨拙,在iOS7.0中苹果公司增加了JS利器JavaScriptCore框架,框架让Objective-C和JavaScript代码直接的交互变得更加的简单方便。该框架其实只是基于webkit中以C/C++实现的JavaScriptCore的一个包装。其本身是可以单独作为一个开发库来使用,框架中有完整的数据计算逻辑,今天只讲H5与本地交互,所以不作涉及,有兴趣可以参考:iOS7新JavaScriptCore框架入门介绍。
JavaScriptCore提供了很多灵活的本地OC与JS的交互方式,通过JSContext和JSValue来完成的,JSContext是一个WebView中js代码运行环境,所有的JS交互都要通过- (JSValue *)evaluateScript:(NSString *)script;方法就可以执行一段JavaScript脚本。
JSValue则可以说是JavaScript和Object-C之间互换的桥梁,它提供了多种方法可以方便地把JavaScript数据类型转换成Objective-C.
具体如何交互我们先来看一段H5代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>测试iOS与JS之前的互调</title>
<style type="text/css">
* {
font-size: 40px;
}
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
function showAppAlertMsg(message){
alert(message);
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div style="margin-top: 100px">
<h1>Test how to use objective-c call js</h1>
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC system camera" onclick="callSystemCamera()">
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC system alert" onclick="showAlertMsg('js title', 'js message')">
</div>
<div>
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC func with JSON " onclick="callWithDict({'name': 'testname', 'age': 10, 'height': 170})">
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC func with JSON and ObjC call js func to pass args." onclick="jsCallObjcAndObjcCallJsWithDict({'name': 'testname', 'age': 10, 'height': 170})">
</div>
<div>
<span id="jsParamFuncSpan" style="color: red; font-size: 50px;"></span>
</div>
</body>
</html>
我们可以看出其中H5实现的JS代码如下:
<script type="text/javascript">
function showAppAlertMsg(message){
alert(message);
}
</script>
函数showAppAlertMsg是H5实现可以由我们本地主动调用的。那么相对应的H5主动调用的方法是:
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC system camera" onclick="callSystemCamera()">
其中callSystemCamera()是H5调用的函数,我们可以看到在HTML代码中是找不到这个函数的实现的,因为这个函数是需要我们本地去实现。
接下来我们就讲一下我们本地如何调用由H5实现的函数showAppAlertMsg,本地如何实现能够右H5端调用的方法:
1.在页面加载完成之后获取JS运行环境JSContext
- (void)webViewDidFinishLoad:(UIWebView *)webView {
JSContext *jsContext = [webView valueForKeyPath:@"documentView.webView.mainFrame.javaScriptContext"];
}
2.利用evaluateScript声明函数并传递参数执行代码
JSValue *jsValue = [jsContext evaluateScript:@"showAppAlertMsg"];
[jsValue callWithArguments:@[@"这是app本地交互文案"]];
第一行代码是声明一个函数showAppAlertMsg,第二行是传递参数并执行代码callWithArguments.
以上是主动调用H5实现的函数,也可以称之为传递数据给H5。
本地实现能够让H5调用的函数:
// 也可以通过下标的方式获取到方法
self.jsContext[@"callSystemCamera"] = ^(){
NSLog(@"callSystemCamera");
};
self.jsContext[@"showAlertMsg"] = ^(NSString *title, NSString *message){
NSLog(@"callSystemCamera");
};
self.jsContext[@"callWithDict"] = ^(id jsonDic){
NSLog(@"callWithDict%@",jsonDic);
};
一目了然,通过Block传递参数和方法。
上面是利用JavaScriptCore的最基本的方法实现JS调用,还有另外一种方案利用JSExport协议进行交互.其实可以理解为通过JSExport协议实现一种把本地的实例绑定为H5中的一个对象,通过这个对象调用本地实例方法的一种交互设计。
该设计在H5端与上面的是不一样的:
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC system camera" onclick="OCModel.callSystemCamera()">
<input type="button" value="Call ObjC system alert" onclick="OCModel.showAlertMsg('js title', 'js message')">
我们会发现 与之前的H5代码相比 多了一个 OCModel,这个在JS中可以理解为一个对象,点击按钮之后调用对象OCModel中的函数OCModel.callSystemCamera,那么该对象如何由本地绑定呢。
1.首先声明一个JSExport协议,该协议需要声明刚才H5中的函数:
#import <JavaScriptCore/JavaScriptCore.h>
@protocol JavaScriptObjectiveCDelegate <JSExport>
// JS调用此方法来调用OC的系统相册方法
- (void)callSystemCamera;
// 在JS中调用时,函数名应该为showAlertMsg(arg1, arg2)
// 这里是只两个参数的。
- (void)showAlert:(NSString *)title msg:(NSString *)msg;
// 通过JSON传过来
- (void)callWithDict:(NSDictionary *)params;
// JS调用Oc,然后在OC中通过调用JS方法来传值给JS。
- (void)jsCallObjcAndObjcCallJsWithDict:(NSDictionary *)params;
@end
2.新建一个类,该类实现上面的协议
@interface NLJsObjCModel : NSObject <JavaScriptObjectiveCDelegate>
@property (nonatomic, weak) JSContext *jsContext;
@property (nonatomic, weak) UIWebView *webView;
@end
实现文件:
#import "NLJsObjCModel.h"
@implementation NLJsObjCModel
- (void)callWithDict:(NSDictionary *)params {
NSLog(@"Js调用了OC的方法,参数为:%@", params);
}
// Js调用了callSystemCamera
- (void)callSystemCamera {
NSLog(@"JS调用了OC的方法,调起系统相册");
// JS调用后OC后,又通过OC调用JS,但是这个是没有传参数的
JSValue *jsFunc = self.jsContext[@"jsFunc"];
[jsFunc callWithArguments:nil];
}
- (void)jsCallObjcAndObjcCallJsWithDict:(NSDictionary *)params {
NSLog(@"jsCallObjcAndObjcCallJsWithDict was called, params is %@", params);
// 调用JS的方法
JSValue *jsParamFunc = self.jsContext[@"jsParamFunc"];
[jsParamFunc callWithArguments:@[@{@"age": @10, @"name": @"lili", @"height": @158}]];
}
- (void)showAlert:(NSString *)title msg:(NSString *)msg {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
UIAlertView *a = [[UIAlertView alloc] initWithTitle:title message:msg delegate:nil cancelButtonTitle:@"Ok" otherButtonTitles:nil, nil];
[a show];
});
}
@end
3.将NLJsObjCModel实例对象绑定到JS中:
#pragma mark - UIWebViewDelegate
- (void)webViewDidFinishLoad:(UIWebView *)webView {
self.jsContext = [webView valueForKeyPath:@"documentView.webView.mainFrame.javaScriptContext"];
// 通过模型调用方法,这种方式更好些。
NLJsObjCModel *model = [[NLJsObjCModel alloc] init];
self.jsContext[@"OCModel"] = model;
model.jsContext = self.jsContext;
model.webView = self.webView;
self.jsContext.exceptionHandler = ^(JSContext *context, JSValue *exceptionValue) {
context.exception = exceptionValue;
NSLog(@"异常信息:%@", exceptionValue);
};
}
到此结束,H5按钮点击之后就可以通过JSExport协议传递跟本地对象,本地对象就能收到相应。
###WKWebView的交互使用
iOS8以后,苹果推出了新框架Wekkit,提供了替换UIWebView的组件WKWebView。
先看下 WKWebView的特性:
- 在性能、稳定性、功能方面有很大提升(最直观的体现就是加载网页是占用的内存,模拟器加载百度与开源中国网站时,WKWebView占用23M,而UIWebView占用85M);
- 允许JavaScript的Nitro库加载并使用(UIWebView中限制);
- 支持了更多的HTML5特性;
- 高达60fps的滚动刷新率以及内置手势;
- 将UIWebViewDelegate与UIWebView重构成了14类与3个协议(查看苹果官方文档);
####WKWebView 的使用呢与UIWebView相同,不同的是回调和代理方法.这里简单介绍一下.
## WKNavigationDelegate
// 页面开始加载时调用
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView didStartProvisionalNavigation:(WKNavigation *)navigation;
// 当内容开始返回时调用
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView didCommitNavigation:(WKNavigation *)navigation;
// 页面加载完成之后调用
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView didFinishNavigation:(WKNavigation *)navigation;
// 页面加载失败时调用
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView didFailProvisionalNavigation:(WKNavigation *)navigation;
####页面跳转的代理方法:
// 接收到服务器跳转请求之后调用
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView didReceiveServerRedirectForProvisionalNavigation:(WKNavigation *)navigation;
// 在收到响应后,决定是否跳转
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView decidePolicyForNavigationResponse:(WKNavigationResponse *)navigationResponse decisionHandler:(void (^)(WKNavigationResponsePolicy))decisionHandler;
// 在发送请求之前,决定是否跳转
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView decidePolicyForNavigationAction:(WKNavigationAction *)navigationAction decisionHandler:(void (^)(WKNavigationActionPolicy))decisionHandler;
####新的 WKUIDelegate协议
这个协议主要用于WKWebView处理web界面的三种提示框(警告框、确认框、输入框),下面是警告框的例子:
/**
* web界面中有弹出警告框时调用
*
* @param webView 实现该代理的webview
* @param message 警告框中的内容
* @param frame 主窗口
* @param completionHandler 警告框消失调用
*/
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView runJavaScriptAlertPanelWithMessage:(NSString *)message initiatedByFrame:(void (^)())completionHandler;
####动态加载并运行JS代码(WKUserScript)
用于在客户端内部加入JS代码,并执行,示例如下
// 图片缩放的js代码
NSString *js = @"var count = document.images.length;for (var i = 0; i < count; i++) {var image = document.images[i];image.style.width=320;};window.alert('找到' + count + '张图');";
// 根据JS字符串初始化WKUserScript对象
WKUserScript *script = [[WKUserScript alloc] initWithSource:js injectionTime:WKUserScriptInjectionTimeAtDocumentEnd forMainFrameOnly:YES];
// 根据生成的WKUserScript对象,初始化WKWebViewConfiguration
WKWebViewConfiguration *config = [[WKWebViewConfiguration alloc] init];
[config.userContentController addUserScript:script];
_webView = [[WKWebView alloc] initWithFrame:self.view.bounds configuration:config];
[_webView loadHTMLString:@"<head></head><imgea src='http://www.nsu.edu.cn/v/2014v3/img/background/3.jpg' />"baseURL:nil];
[self.view addSubview:_webView];
五、webView 执行JS代码
用户调用用JS写过的代码,一般指服务端开发的:
//javaScriptString是JS方法名,completionHandler是异步回调block
[self.webView evaluateJavaScript:javaScriptString completionHandler:completionHandler];
六、JS调用App注册过的方法
在WKWebView里面注册供JS调用的方法,是通过WKUserContentController类下面的方法:
- (void)addScriptMessageHandler:(id <WKScriptMessageHandler>)scriptMessageHandler name:(NSString *)name;
scriptMessageHandler是代理回调,JS调用name方法后,OC会调用scriptMessageHandler指定的对象。
JS在调用OC注册方法的时候要用下面的方式:
window.webkit.messageHandlers.<name>.postMessage(<messageBody>)
注意,name(方法名)是放在中间的,在这里个人理解该name可以理解为一个标识,该标识将OC本地的实例对象绑定到JS中,将messageBody只能是一个对象,如果要传多个值,需要封装成数组,或者字典。整个示例如下:
//OC注册供JS调用的方法
[[_webView configuration].userContentController addScriptMessageHandler:self name:@"app"];
//OC在JS调用方法做的处理
- (void)userContentController:(WKUserContentController *)userContentController didReceiveScriptMessage:(WKScriptMessage *)message
{
NSLog(@"JS 调用了 %@ 方法,传回参数 %@",message.name,message.body);
}
//JS调用
window.webkit.messageHandlers.app.postMessage(null);
##最后:
简单做一个总结,在iOS7以前我们只能使用UIWebView,所以在js交互中只能通过stringByEvaluatingJavaScriptFromString进行本地调用H5,而H5端调用本地多采用URLSchemes方式(解耦---Hybrid H5跨平台性思考),
iOS7之后使用UIWebView则可以使用JavaScriptCore框架,通过JSContext进行JS交互。
iOS8之后可以使用WKWebView本身的框架,毕竟WKWebView本身已经优化很多,并且提供了更多的方法和协议,不过注意一点的是在WKWebView中鉴于一些线程和进程的问题是无法获取JSContext的。
JavaScriptCore框架在iOS7中的对象交互和管理教程
上一篇文章中已经简单入门了iOS7中新加的JavaScriptCore框架的基本用法,十分的简单方便而且高效,不过也仅限于数值型、布尔型、字符串、数组等这些基础类型。本文将扩展到更复杂的类型,介绍一下该强大的框架是如何让Objective-C对象和JavaScript对象进行直接互通的。
为了方便起见,以下所有代码中的JSContext对象都会添加如下的log方法和eventHandler
JSContext *context = [[JSContext alloc] init];
context.exceptionHandler = ^(JSContext *con, JSValue *exception) {
NSLog(@"%@", exception);
con.exception = exception;
};
context[@"log"] = ^() {
NSArray *args = [JSContext currentArguments];
for (id obj in args) {
NSLog(@"%@",obj);
}
};
##键值对编程—Dictionary
JSContext并不能让Objective-C和JavaScript的对象直接转换,毕竟两者的面向对象的设计方式是不同的:前者基于class,后者基于prototype。但所有的对象其实可以视为一组键值对的集合,所以JavaScript中的对象可以返回到Objective-C中当做NSDictionary类型进行访问。
JSValue * obj = [context evaluateScript: @ "var jsObj = {number: 7, name: 'Ider'}; jsObj"];
NSLog (@ "% @,% @", obj [@ "name"], obj [@ 'number']);
NSDictionary * dic = [obj toDictionary];
NSLog (@ "% @,% @", dic [@ "name"], dic [@ 'number']);
/ / Output:
/ / Ider, 7
/ / Ider, 7
同样的,NSDicionary和NSMutableDictionary传入到JSContext之后也可以直接当对象来调用:
NSDictionary * dic = @ @ {"name": @ "Ider", @ "#": @ (21)};
context [@ "dic"] = dic;
[Context evaluateScript: @ "log (dic.name, dic ['#'])"];
/ / Output:
/ / Ider
/ / 21
##语言穿梭机—JSExport协议
JavaScript可以脱离prototype继承完全用JSON来定义对象,但是Objective-C编程里可不能脱离类和继承了写代码。所以JavaScriptCore就提供了JSExport作为两种语言的互通协议。JSExport中没有约定任何的方法,连可选的(@optional)都没有,但是所有继承了该协议(@protocol)的协议(注意不是Objective-C的类(@interface))中定义的方法,都可以在JSContext中被使用。语言表述起来有点绕,还是用例子来说明会更明确一点。
@protocol PersonProtocol <JSExport>
@property (nonatomic, retain) NSDictionary *urls;
- (NSString *)fullName;
@end
@interface Person :NSObject <PersonProtocol>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *lastName;
@end;
@implementation Person
@synthesize firstName, lastName, urls;
- (NSString *)fullName {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", self.firstName, self.lastName];
}
@end
在上边的代码中,定义了一个PersonProtocol,并让它继承了神秘的JSExport协议,在新定义的协议中约定urls属性和fullName方法。之后又定义了Person类,除了让它实现PersonProtocol外,还定义了firstName和lastName属性。而fullName方法返回的则是两部分名字的结合。
下边就来创建一个Person对象,然后传入到JSContext中并尝试使用JavaScript来访问和修改该对象。
/ / Initialize target person
Person * person = [ [ Person alloc ] init ];
context [@ "p" ] = person ;
person.firstName = @ " Idera ";
person.lastName = @ " Zheng ";
person.urls @ = @ { "site " : @ " http://www.iderzheng.com "} ;
/ / Ok to get FullName
[ evaluateScript context : @ " log ( p.fullName () ); " ];
/ / Can not access firstname
[ evaluateScript context : @ " log ( p.firstName ) " ];
/ / Ok to access object as dictionary
[ evaluateScript context : @ " log ( ' site: ' p.urls.site , ' blog: ' p.urls.blog ) " ];
/ / Ok to change urls property
[ evaluateScript context : @ " = { p.urls blog: ' http://blog.iderzheng.com ' }" ];
[ evaluateScript context : @ " log ( ' ------- ------- AFTER CHANGE URLS ' ) " ];
[ evaluateScript context : @ " log ( ' site: ' p.urls.site , ' blog: ' p.urls.blog ) " ];
/ / Affect on Objective- C side as well
NSLog (@ " % @ " , person.urls );
/ / Output :
/ / IDER Zheng
/ / Undefined
/ / Undefined
/ / Site :
/ / Http://www.iderzheng.com
/ / Blog:
/ / Undefined
/ / ------- ------- AFTER CHANGE URLS
/ / Site :
/ / Undefined
/ / Blog:
/ / Http://blog.iderzheng.com
/ / {
/ / Blog = " http://blog.iderzheng.com ";
/ / }
从输出结果不难看出,当访问firstName和lastName的时候给出的结果是undefined,因为它们跟JavaScript没有JSExport的联系。但这并不影响从fullName()中正确得到两个属性的值。和之前说过的一样,对于NSDictionary类型的urls,可以在JSContext中当做对象使用,而且还可以正确地给urls赋予新的值,并反映到实际的Objective-C的Person对象上。
JSExport不仅可以正确反映属性到JavaScript中,而且对属性的特性也会保证其正确,比如一个属性在协议中被声明成readonly,那么在JavaScript中也就只能读取属性值而不能赋予新的值。
对于多参数的方法,JavaScriptCore的转换方式将Objective-C的方法每个部分都合并在一起,冒号后的字母变为大写并移除冒号。比如下边协议中的方法,在JavaScript调用就是:doFooWithBar(foo, bar);
@protocol MultiArgs <JSExport>
- (void)doFoo:(id)foo withBar:(id)bar;
@end
如果希望方法在JavaScript中有一个比较短的名字,就需要用的JSExport.h中提供的宏:JSExportAs(PropertyName, Selector)。
@protocol LongArgs <JSExport>
JSExportAs(testArgumentTypes,
- (NSString *)testArgumentTypesWithInt:(int)i double:(double)d
boolean:(BOOL)b string:(NSString *)s number:(NSNumber *)n
array:(NSArray *)a dictionary:(NSDictionary *)o
);
@end
比如上边定义的协议中的方法,在JavaScript就只要用testArgumentTypes(i, d, b, s, n, a, dic);来调用就可以了。
虽然JavaScriptCore框架还没有官方编程指南,但是在JSExport.h文件中对神秘协议的表述还是比较详细的,其中有一条是这样描述的:
By default no methods or properties of the Objective-C class will be exposed to JavaScript, however methods and properties may explicitly be exported. For each protocol that a class conforms to, if the protocol incorporates the protocol JSExport, then the protocol will be interpreted as a list of methods and properties to be exported to JavaScript.
这里面有个incorporate一词值得推敲,经过验证只有直接继承了JSExport的自定义协议(@protocol)才能在JSContext中访问到。也就是说比如有其它的协议继承了上边的PersonProtocol,其中的定义的方法并不会被引入到JSContext中。从源码中也能看出JavaScriptCore框架会通过class_copyProtocolList方法找到类所遵循的协议,然后再对每个协议通过protocol_copyProtocolList检查它是否遵循JSExport协议进而将方法反映到JavaScript之中。
##对已定义类扩展协议— class_addProtocol
对于自定义的Objective-C类,可以通过之前的方式自定义继承了JSExport的协议来实现与JavaScript的交互。对于已经定义好的系统类或者从外部引入的库类,她们都不会预先定义协议提供与JavaScript的交互的。好在Objective-C是可以在运行时实行对类性质的修改的。
比如下边的例子,就是为UITextField添加了协议,让其能在JavaScript中可以直接访问text属性。该接口如下:
@protocol JSUITextFieldExport <JSExport>
@property(nonatomic,copy) NSString *text;
@end
之后在通过class_addProtocol为其添加上该协议:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
textField.text = @"7";
class_addProtocol([UITextField class], @protocol(JSUITextFieldExport));
}
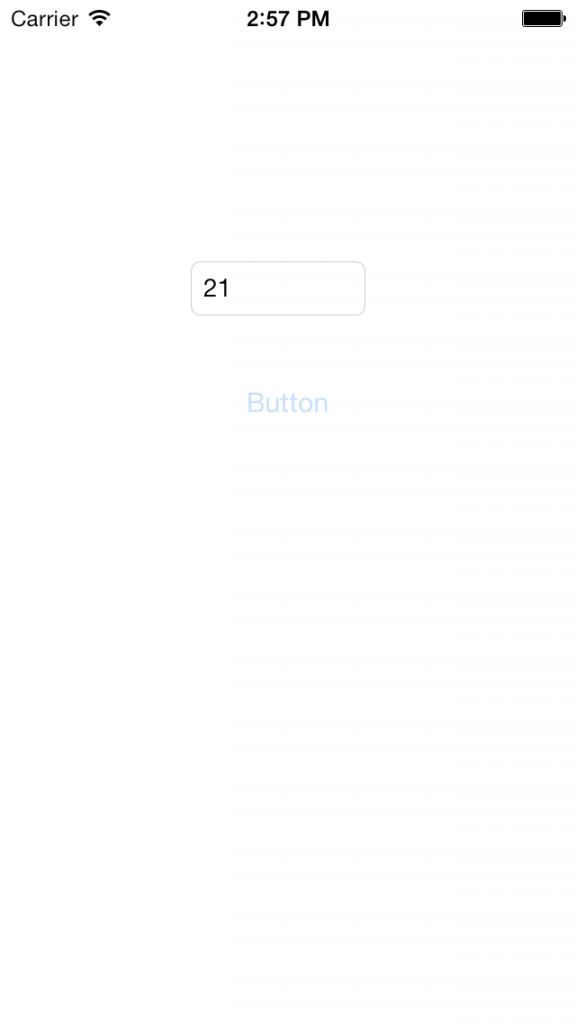
为一个UIButton添加如下的事件,其方法只要是将textField传入到JSContext中然后读取其text值,自增1后重新赋值:
- (IBAction)pressed:(id)sender {
JSContext *context = [[JSContext alloc] init];
context[@"textField"] = textField;
NSString *script = @"var num = parseInt(textField.text, 10);"
"++num;"
"textField.text = num;";
[context evaluateScript:script];
}
当运行点击UIButton时就会看到UITextField的值在不断增加,也证明了对于已定义的类,也可以在运行时添加神奇的JSExport协议让它们可以在Objective-C和JavaScript直接实现友好互通。

##Garbage Collection(垃圾回收机制)
虽然Objetive-C和JavaScript都是面向对象的语言,而且它们都可以让程序员专心于业务逻辑,不用担心内存回收的问题。但是两者的内存回首机制全是不同的,Objective-C是基于引用计数,之后Xcode编译器又支持了自动引用计数(ARC, Automatic Reference Counting);JavaScript则如同Java/C#那样用的是垃圾回收机制(GC, Garbage Collection)。当两种不同的内存回收机制在同一个程序中被使用时就难免会产生冲突。
比如,在一个方法中创建了一个临时的Objective-C对象,然后将其加入到JSContext放在JavaScript中的变量中被使用。因为JavaScript中的变量有引用所以不会被释放回收,但是Objective-C上的对象可能在方法调用结束后,引用计数变0而被回收内存,因此JavaScript层面也会造成错误访问。
同样的,如果用JSContext创建了对象或者数组,返回JSValue到Objective-C,即使把JSValue变量retain下,但可能因为JavaScript中因为变量没有了引用而被释放内存,那么对应的JSValue也没有用了。
怎么在两种内存回收机制中处理好对象内存就成了问题。JavaScriptCore提供了JSManagedValue类型帮助开发人员更好地管理对象内存。
@interface JSManagedValue : NSObject
// Convenience method for creating JSManagedValues from JSValues.
+ (JSManagedValue *)managedValueWithValue:(JSValue *)value;
// Create a JSManagedValue.
- (id)initWithValue:(JSValue *)value;
// Get the JSValue to which this JSManagedValue refers. If the JavaScript value has been collected,
// this method returns nil.
- (JSValue *)value;
@end
在《iOS7新JavaScriptCore框架入门介绍》有提到JSVirtualMachine为整个JavaScriptCore的执行提供资源,所以当将一个JSValue转成JSManagedValue后,就可以添加到JSVirtualMachine中,这样在运行期间就可以保证在Objective-C和JavaScript两侧都可以正确访问对象而不会造成不必要的麻烦。
@interface JSVirtualMachine : NSObject
// Create a new JSVirtualMachine.
- (id)init;
// addManagedReference:withOwner and removeManagedReference:withOwner allow
// clients of JSVirtualMachine to make the JavaScript runtime aware of
// arbitrary external Objective-C object graphs. The runtime can then use
// this information to retain any JavaScript values that are referenced
// from somewhere in said object graph.
//
// For correct behavior clients must make their external object graphs
// reachable from within the JavaScript runtime. If an Objective-C object is
// reachable from within the JavaScript runtime, all managed references
// transitively reachable from it as recorded with
// addManagedReference:withOwner: will be scanned by the garbage collector.
//
- (void)addManagedReference:(id)object withOwner:(id)owner;
- (void)removeManagedReference:(id)object withOwner:(id)owner;
@end
##了解更多更多—Source Code
对于iOS7提供JavaScriptCore已经介绍的差不多了,之前也提到这其实是一个开源的框架,所以如果想要在低版本的iOS上使用,也可以很容易地自行添加源码进行编译和使用。
阅读源码也可以更加了解JavaScriptCore是怎么实现的,在开发时候也可以注意到更多的细节避免错误的发生,想要阅读框架的源码可以在这里(源码1,源码2,源码3)。
文章中的代码和例子都比较简单,如果想了解更多JavaScriptCore的使用方法,在这里有详细的测试案例可以提供一些线索。不过经验证并不是所有的测试案例在iOS7中都会通过,这大概是测试案例所用的JavaScriptCore是为chromium实现的而iOS7是webkit吧。
References:
1 Steamclock Software – Apple’s new Objective-C to Javascript Bridge
2 JavaScriptCore and iOS 7 » Big Nerd Ranch BlogBig Nerd Ranch Blog
3 IOS7开发~JavaScriptCore (二) – 阿福的专栏 – 博客频道 – CSDN.NET
4 API in trunk/Source/JavaScriptCore – WebKit
5 Objective-C Runtime Reference
6 Automatic Reference Counting vs. Garbage Collection – The Oxygene Language Wiki
Copyright © 2015 Powered by MWeb, 豫ICP备09002885号-5